11 Prickly Pear Facts For Better Health
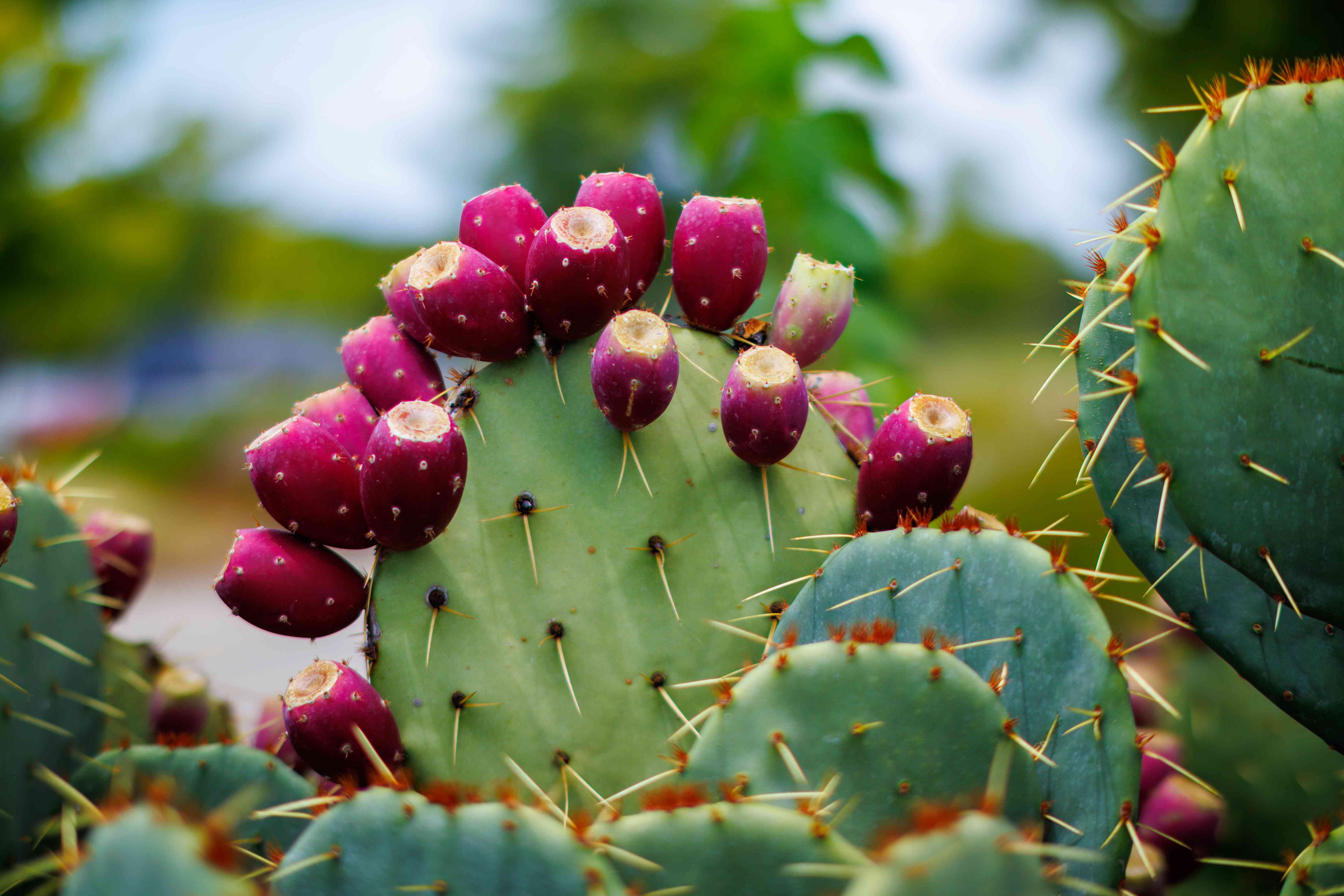

The prickly pear cactus, a plant often overlooked despite its vibrant flowers and nutritious fruits, holds a treasure trove of health benefits waiting to be uncovered. Native to the Americas, this unique cactus has been a cornerstone of traditional medicine and nutrition for centuries, particularly among indigenous communities. Let’s delve into 11 fascinating facts about the prickly pear, exploring its history, nutritional profile, and the various ways it can contribute to better health.
Nutritional Powerhouse: The prickly pear fruit, often referred to as a tuna in Spanish, is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It’s an excellent source of vitamin C, magnesium, and potassium, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. The fruit’s high water content also contributes to its potential benefits for hydration and digestion.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Studies have shown that compounds found in the prickly pear have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help in reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms associated with conditions like arthritis. The flavonoids, ascorbic acid, and betalains present in the cactus are key contributors to its anti-inflammatory effects.
Wound Healing and Skin Health: The gel of the prickly pear cactus has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat wounds, burns, and skin irritations due to its moisturizing and protective properties. Its application can help in speeding up the healing process and reducing the risk of infection.
Potential Anti-Diabetic Effects: Research suggests that the prickly pear may have a beneficial effect on blood sugar levels. The fiber and pectin in the fruit can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, potentially helping in managing type 2 diabetes. However, more studies are needed to confirm its efficacy and safety for this use.
Hangover Relief: In some cultures, the prickly pear is used as a hangover remedy. The components of the cactus may help in reducing the severity of hangover symptoms by decreasing inflammation and protecting the liver. While anecdotal evidence supports its use, scientific studies to confirm its effectiveness are limited.
Supports Healthy Gut Bacteria: The prebiotic fiber in prickly pear fruits can help feed the good bacteria in the gut, supporting a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut microbiota is crucial for immune function, digestion, and even mental health.
Antioxidant Rich: The prickly pear is packed with antioxidants, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and betalains, which can help protect the body against free radicals. This antioxidant activity can contribute to reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
May Help Lower Cholesterol: Some studies indicate that regular consumption of prickly pear can help in lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease. The soluble fiber in the fruit is believed to play a significant role in this effect by binding to bile acids and removing them from the body, which in turn leads to the liver using more cholesterol to produce bile, thereby lowering cholesterol levels.
Rich in Fiber: With its high fiber content, the prickly pear can contribute to digestive health, promote satiety, and support healthy blood sugar levels. Incorporating foods high in dietary fiber like the prickly pear into one’s diet can have significant benefits for overall health and well-being.
Cosmetic and Skin Care Uses: Beyond its internal health benefits, the prickly pear cactus is used in cosmetics and skin care products due to its moisturizing, anti-aging, and protective effects on the skin. Its oil, extracted from the seeds, is particularly valued for its high content of fatty acids and antioxidants, making it an excellent ingredient for skin care regimens.
Sustainable and Versatile: The prickly pear cactus is not only a valuable source of nutrition and health benefits but also a symbol of sustainability. It requires minimal water to grow, can thrive in poor soil, and provides habitat and food for various wildlife. Its pads can be used as a natural fence, and its fruits, flowers, and pads are edible, making it a versatile and environmentally friendly crop.
What are the potential side effects of consuming prickly pear?
+While generally considered safe, consuming prickly pear can cause stomach upset in some individuals, particularly when eaten in large quantities. It's also important to properly clean and prepare the fruits and pads to avoid ingesting spines or other harmful parts.
Can prickly pear be used as a treatment for diabetes?
+While there is some evidence suggesting that prickly pear may help in managing blood sugar levels, it should not be used as a replacement for conventional diabetes treatment without consulting a healthcare provider. It may be considered as a complementary therapy under medical supervision.
How can I incorporate prickly pear into my diet?
+The prickly pear fruits can be eaten raw, used in jams, or as a topping for salads and yogurt. The pads can be grilled, sautéed, or used in soups and stews. Prickly pear juice and supplements are also available for those looking for alternative ways to benefit from its nutritional profile.
In conclusion, the prickly pear cactus, with its multitude of health benefits and sustainable characteristics, is truly a remarkable plant. By understanding and harnessing its power, individuals can make informed choices about their health and well-being, while also supporting environmentally friendly practices. Whether through its nutritional value, traditional medicinal uses, or its potential in managing chronic diseases, the prickly pear is a valuable resource that deserves our attention and appreciation. As we continue to explore and learn more about this incredible cactus, its role in promoting better health and sustainability is likely to expand, offering us a natural and effective way to enhance our quality of life.