12 Heart Attack Causes You Must Know
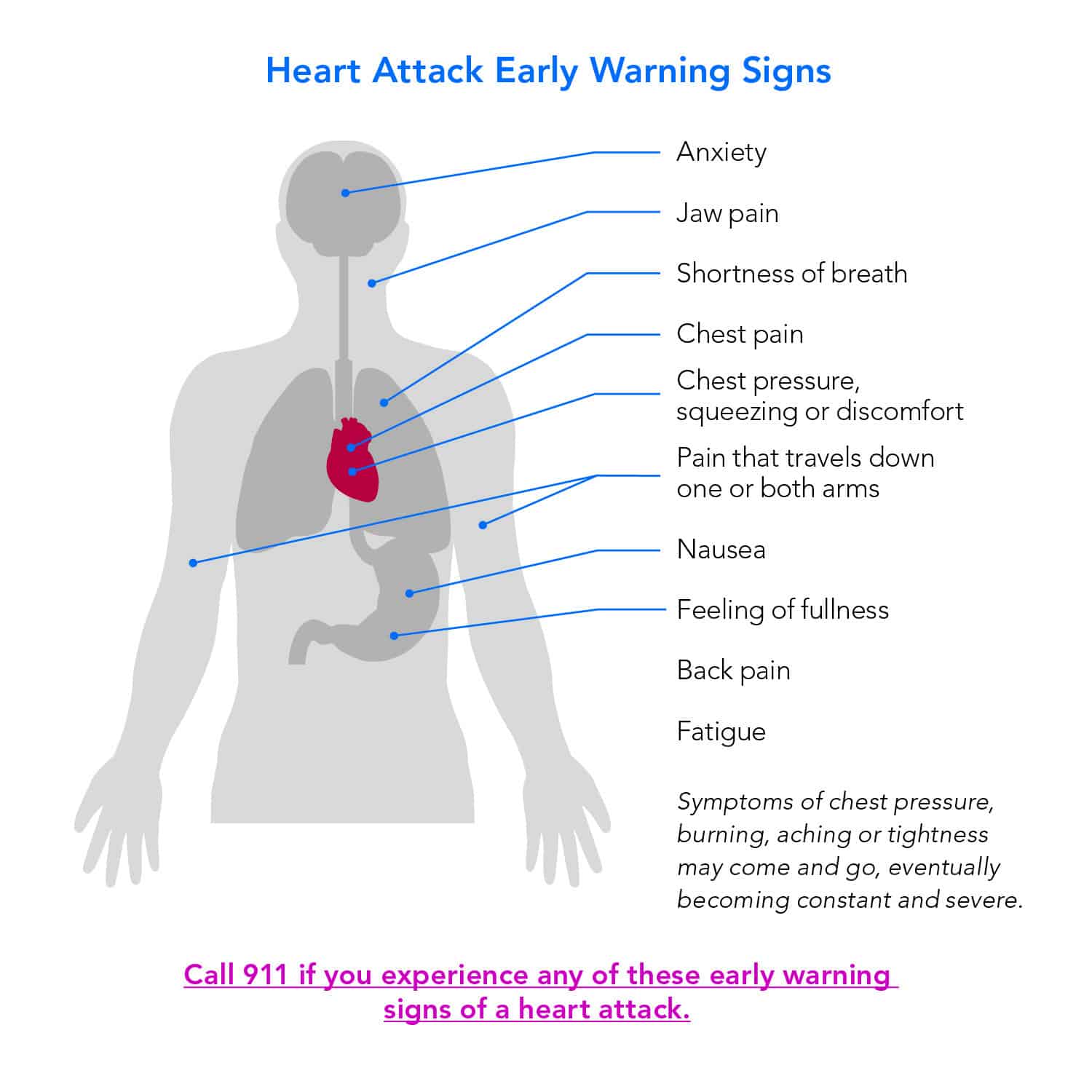
The sudden onset of a heart attack can be a devastating and life-altering event, not just for the individual experiencing it, but also for their loved ones. Understanding the causes of a heart attack is crucial for prevention, early intervention, and effective management. At the core of a heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, is the interruption of blood flow to the heart, leading to damage or death of heart muscle cells. This interruption is most commonly caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. Over time, a condition known as atherosclerosis can lead to the buildup of plaque (a mix of fat, cholesterol, and other substances) in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. If the plaque ruptures, a blood clot can form, blocking the artery and causing a heart attack.
1. High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart disease and heart attacks. It causes the heart to work harder, which can lead to thickening of the heart muscle. Over time, high blood pressure can also cause the coronary arteries to become narrowed and hardened, reducing blood flow to the heart. According to the American Heart Association, nearly half of adults in the United States have hypertension. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication is crucial for reducing the risk of heart attacks.
2. High Cholesterol
High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack. Conversely, high levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or “good” cholesterol, can help remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. Foods high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels. Therefore, dietary adjustments and, in some cases, cholesterol-lowering medications are important for managing cholesterol levels.
3. Smoking
Smoking tobacco is a significant risk factor for heart disease and heart attacks. It damages the inner lining of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the accumulation of plaque. Smoking also increases blood pressure, lowers HDL cholesterol, and makes blood more likely to clot, all of which can lead to a heart attack. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease and is considered one of the most effective ways to prevent a heart attack.
4. Obesity
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing conditions that lead to heart attacks, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Excess weight, particularly around the waist, can also lead to inflammation, which is linked to heart disease. Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help with weight management and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes, especially if not well-managed, can lead to high blood sugar levels, which, over time, can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing conditions that can lead to a heart attack. Managing diabetes through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing complications like heart disease.
6. Family History
Having a family history of heart disease can increase an individual’s risk of experiencing a heart attack. This risk is higher if the family member had heart disease at a young age. Genetic factors can influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and other risk factors for heart disease. While you can’t change your family history, being aware of it can motivate you to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle and, if necessary, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage risk factors.
7. Lack of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help manage and reduce risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. It can also improve circulation, increase the efficiency of oxygen use, and enhance overall cardiovascular health. A sedentary lifestyle, on the other hand, is associated with an increased risk of heart attacks. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of both, per week, is recommended for adults.
8. Stress
Chronic stress can increase the risk of a heart attack by raising blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease, and influencing behaviors such as smoking, overeating, and physical inactivity. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate its effects on heart health.
9. Certain Medications and Supplements
Some medications and supplements, especially when used improperly or in excess, can increase the risk of a heart attack by affecting blood pressure, heart rate, and blood clotting. It’s essential to use medications and supplements under the guidance of a healthcare provider and to discuss any potential risks, especially if you have existing heart conditions.
10. Previous Heart Attack or Stroke
Having had a previous heart attack or stroke significantly increases the risk of having another event. This is because the underlying conditions that led to the first event, such as narrowed arteries, are likely still present. Comprehensive management of risk factors and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for preventing recurrent events.
11. Age
The risk of heart attack increases with age. Men aged 45 and older and women aged 55 and older are at greater risk. Age cannot be changed, but being aware of the increased risk with age can prompt individuals to pay closer attention to other risk factors and take preventive measures.
12. Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, a condition that causes pauses in breathing during sleep, can increase the risk of heart attack. It is associated with high blood pressure, inflammation, and other conditions that can lead to heart disease. Treating sleep apnea, often through the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine or lifestyle changes, can help reduce this risk.
Understanding and Managing Risk Factors
Understanding these causes and risk factors is the first step towards prevention and management. Not everyone who has a heart attack will have shown previous signs of heart disease, but for many, there will have been recognizable risk factors. By modifying lifestyle habits, such as diet and physical activity, managing conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing a heart attack. Regular health check-ups can also help identify risk factors early, allowing for timely intervention.
Conclusion
A heart attack is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack and seeking help promptly can save lives. The American Heart Association recommends remembering the acronym “FAST” to identify signs of a stroke or heart attack: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, and Time to call for emergency services. However, prevention remains the best strategy. By understanding the causes of heart attacks and taking proactive steps to manage risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of experiencing such an event and maintain a healthier, more resilient heart.
What are the most common symptoms of a heart attack?
+The most common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort that feels like pressure, tightness, pain, or a squeezing or aching sensation in the chest or arms, which may spread to the neck, jaw, or back. Shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness are also common symptoms. Women are more likely than men to experience other symptoms, such as shortness of breath and pain in the stomach or back.
How can I reduce my risk of having a heart attack?
+Reducing your risk of having a heart attack involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a healthy diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Regular physical activity, not smoking, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and controlling conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes are also crucial.
What should I do if I think I'm having a heart attack?
+If you think you're having a heart attack, call your local emergency number immediately. In the U.S., this is 911. If you're in a country with a different emergency number, be sure to know what it is and use it. Do not attempt to drive yourself to the hospital. While waiting for help to arrive, chew an aspirin if your doctor has recommended this as part of your heart health plan. Aspirin can help reduce the severity of a heart attack.
Implementing lifestyle changes and being proactive about managing risk factors can significantly reduce the risk of a heart attack. By understanding the causes and taking steps towards prevention, individuals can lead healthier lives and minimize the risk of this potentially devastating event.