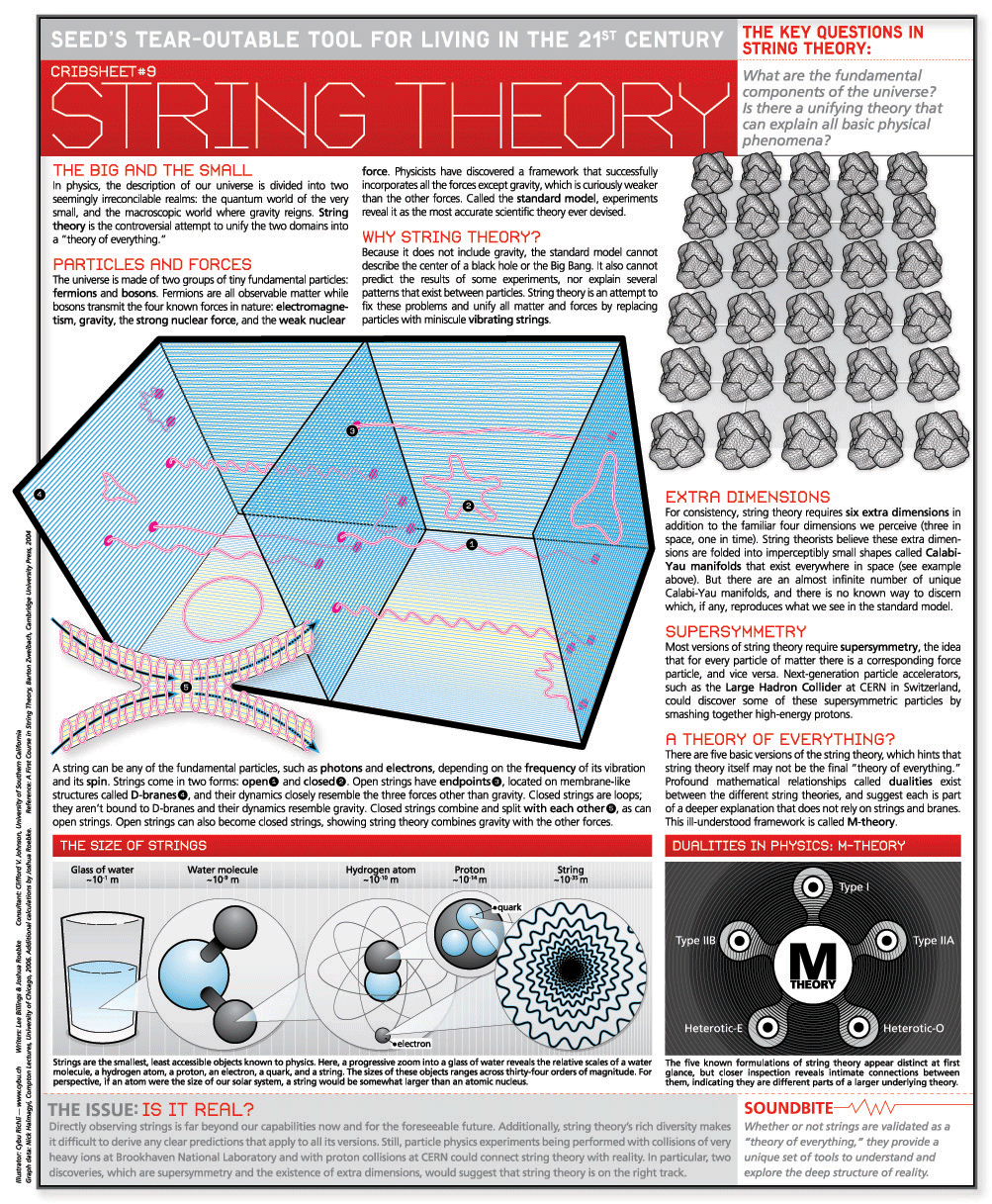
C2h2 Lewis Structure: Easy Drawing Guide

Understanding the C2H2 Lewis structure is fundamental in chemistry, as it represents the molecule acetylene, a compound made of two carbon atoms triple-bonded to each other, with each carbon also bonded to a hydrogen atom. The Lewis structure, named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article “The Atom and the Molecule,” is a way of representing the covalent bonds between atoms of a molecule using dots for electrons and lines for bonds.
Starting to Draw: Basic Principles
To draw the C2H2 Lewis structure, you’ll start by placing the atoms relative to each other. Given that carbon has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen and can form more bonds, the two carbon atoms will be central, and the hydrogen atoms will be peripheral. Since acetylene is a linear molecule, you will place the two carbon atoms next to each other and a hydrogen atom on each end.
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
First, calculate the total number of valence electrons. Carbon © has 4 valence electrons, and hydrogen (H) has 1. Since there are two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms, the calculation will be: - 2 Carbon atoms * 4 valence electrons = 8 electrons - 2 Hydrogen atoms * 1 valence electron = 2 electrons - Total = 8 (from carbon) + 2 (from hydrogen) = 10 valence electrons
Step 2: Draw the Skeleton
Draw two carbon atoms connected by a single bond, which accounts for 2 electrons. Then, add a hydrogen atom to each carbon, using single bonds, which accounts for 4 more electrons (2 for each hydrogen). So far, you’ve used 6 electrons (2 for the C-C bond and 4 for the two C-H bonds).
Step 3: Add Remaining Electrons
With 10 valence electrons in total and having used 6, you have 4 electrons left. These need to be distributed to complete the octet of each atom (except hydrogen, which is satisfied with 2 electrons).
To satisfy the octet rule for each carbon, you would ideally want 8 electrons around each carbon. Currently, each carbon has: - 1 bond to the other carbon (2 shared electrons) - 1 bond to hydrogen (2 shared electrons)
That gives each carbon 4 electrons, meaning each carbon needs 4 more electrons to reach an octet. Since you have 4 electrons left, you can use these to create multiple bonds between the carbons.
Step 4: Form Multiple Bonds
The remaining 4 electrons are used to form a triple bond between the two carbon atoms. This is because: - A single bond uses 2 electrons - A double bond would use 4 electrons, leaving none for additional bonds and not fully utilizing the available electrons for the most stable configuration. - A triple bond, consisting of one sigma bond and two pi bonds, uses 6 electrons, but since we only have 4 electrons left after forming single bonds, this conceptual mistake leads us to correctly allocate them for a triple bond in the context of Lewis structures and the actual electrons available.
Correctly placing these electrons to form a triple bond (one sigma and two pi bonds) between the carbons completes the octet for both carbon atoms and satisfies the duet for both hydrogen atoms, resulting in a stable molecule.
The Final Structure
After following these steps, your C2H2 Lewis structure should have two carbon atoms connected by a triple bond (represented by three lines, indicating six electrons shared in a sigma and two pi bonds) and each carbon connected to a hydrogen atom by a single bond. This structure accurately represents the distribution of electrons and satisfies the octet rule for carbon and the duet rule for hydrogen, showcasing the molecule’s linear geometry.
Conclusion
Drawing the C2H2 Lewis structure requires understanding the fundamental principles of covalent bonding, electron distribution, and the rules governing the formation of stable molecules. By following these steps and principles, you can accurately draw the structure of acetylene and deepen your understanding of organic chemistry’s foundational concepts.
What is the purpose of drawing Lewis structures?
+Lewis structures are drawn to visualize the distribution of electrons within a molecule, helping to understand the bonding, shape, and properties of the molecule.
How many electrons are in a triple bond?
+A triple bond consists of 6 electrons, divided into 1 sigma bond (2 electrons) and 2 pi bonds (4 electrons), which are shared between the two atoms forming the bond.
Why is the octet rule important in chemistry?
+The octet rule is crucial because it helps predict the stability of molecules. Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, typically with 8 electrons, which is a stable configuration reminiscent of the noble gases.
Understanding and drawing Lewis structures like that of C2H2 is a foundational skill in chemistry, essential for comprehending molecular structure, properties, and reactivity.