Displacement: Calculate Distance Easily
Displacement, a fundamental concept in physics, is the shortest distance between an object’s initial and final positions. Understanding displacement is crucial for calculating distances, velocities, and other physical quantities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of displacement, exploring its definition, formula, and applications, as well as providing practical examples and step-by-step calculations to help you easily calculate distances.
Introduction to Displacement
Displacement is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (amount of movement) and direction. It is often denoted by the symbol Δs (delta s) or simply d. The displacement of an object can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on the direction of movement relative to the reference frame. For instance, if an object moves 5 meters to the right and then 3 meters to the left, its total displacement would be 2 meters to the right.
Calculating Displacement
The formula to calculate displacement is:
Displacement (d) = Final Position (x₂) - Initial Position (x₁)
d = x₂ - x₁
Where x₁ and x₂ are the initial and final positions of the object, respectively.
To illustrate this concept, let’s consider a real-world example. Suppose you are driving from City A to City B, covering a total distance of 250 kilometers. However, due to traffic congestion, you take a detour, which adds an extra 20 kilometers to your journey. In this case, your total distance traveled would be 270 kilometers, but your displacement would still be 250 kilometers, as you ended up at your intended destination, City B.
Types of Displacement
There are two primary types of displacement: linear displacement and angular displacement.
- Linear Displacement: This refers to the displacement of an object in a straight line. It is the most common type of displacement and is calculated using the formula: d = x₂ - x₁.
- Angular Displacement: This refers to the displacement of an object in a rotational motion. It is calculated using the formula: θ = θ₂ - θ₁, where θ is the angle of rotation.
Applications of Displacement
Displacement has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Physics and Engineering: Displacement is used to calculate velocities, accelerations, and forces.
- Navigation and Transportation: Displacement is used to determine the shortest distance between two points, which is essential for navigation and transportation systems.
- Computer Science: Displacement is used in graphics and game development to create realistic animations and simulations.
Step-by-Step Calculation of Displacement
Here’s a step-by-step example to calculate the displacement of an object:
- Identify the initial and final positions of the object.
- Determine the direction of movement relative to the reference frame.
- Calculate the displacement using the formula: d = x₂ - x₁.
- Consider any external factors that may affect the displacement, such as friction or air resistance.
For instance, suppose an object moves from position x₁ = 10 meters to position x₂ = 25 meters. To calculate the displacement, we would use the formula:
d = x₂ - x₁ = 25 - 10 = 15 meters
Therefore, the displacement of the object is 15 meters.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
+Distance refers to the total length of the path traveled by an object, while displacement refers to the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of the object.
How do I calculate displacement in a 2D plane?
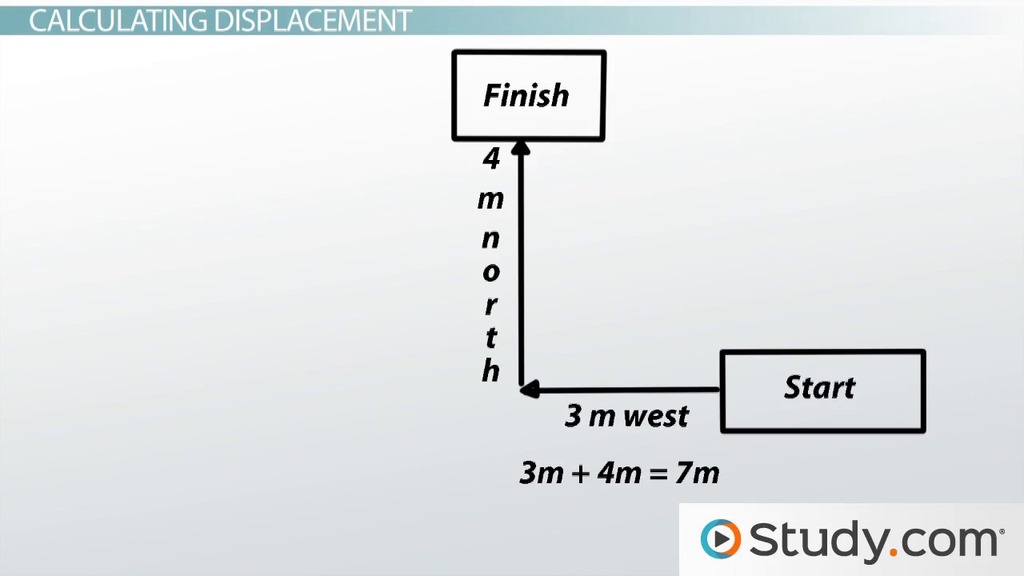
+To calculate displacement in a 2D plane, you need to use the Pythagorean theorem: d = √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²), where x and y are the coordinates of the initial and final positions.
What are some real-world applications of displacement?
+Displacement has numerous applications in physics, engineering, navigation, and transportation. It is used to calculate velocities, accelerations, and forces, as well as to determine the shortest distance between two points.
Conclusion
In conclusion, displacement is a fundamental concept in physics that is essential for calculating distances, velocities, and other physical quantities. By understanding the definition, formula, and applications of displacement, you can easily calculate distances and solve complex problems. Remember to consider the direction of movement relative to the reference frame and to use the correct formula for calculating displacement. With practice and patience, you can become proficient in calculating displacement and applying it to real-world problems.
Additional Resources
For further learning, we recommend exploring the following resources:
- Physics textbooks: “Physics for Scientists and Engineers” by Paul A. Tipler and Gene Mosca, “Fundamentals of Physics” by David Halliday, Robert Resnick, and Jearl Walker.
- Online tutorials: Khan Academy, Coursera, edX.
- Real-world examples: Navigate through Google Maps or GPS devices to see how displacement is used in navigation systems.
By mastering the concept of displacement, you can gain a deeper understanding of the physical world and develop problem-solving skills that can be applied to various fields.



