R In Ideal Gas Law: Simplify Calculations
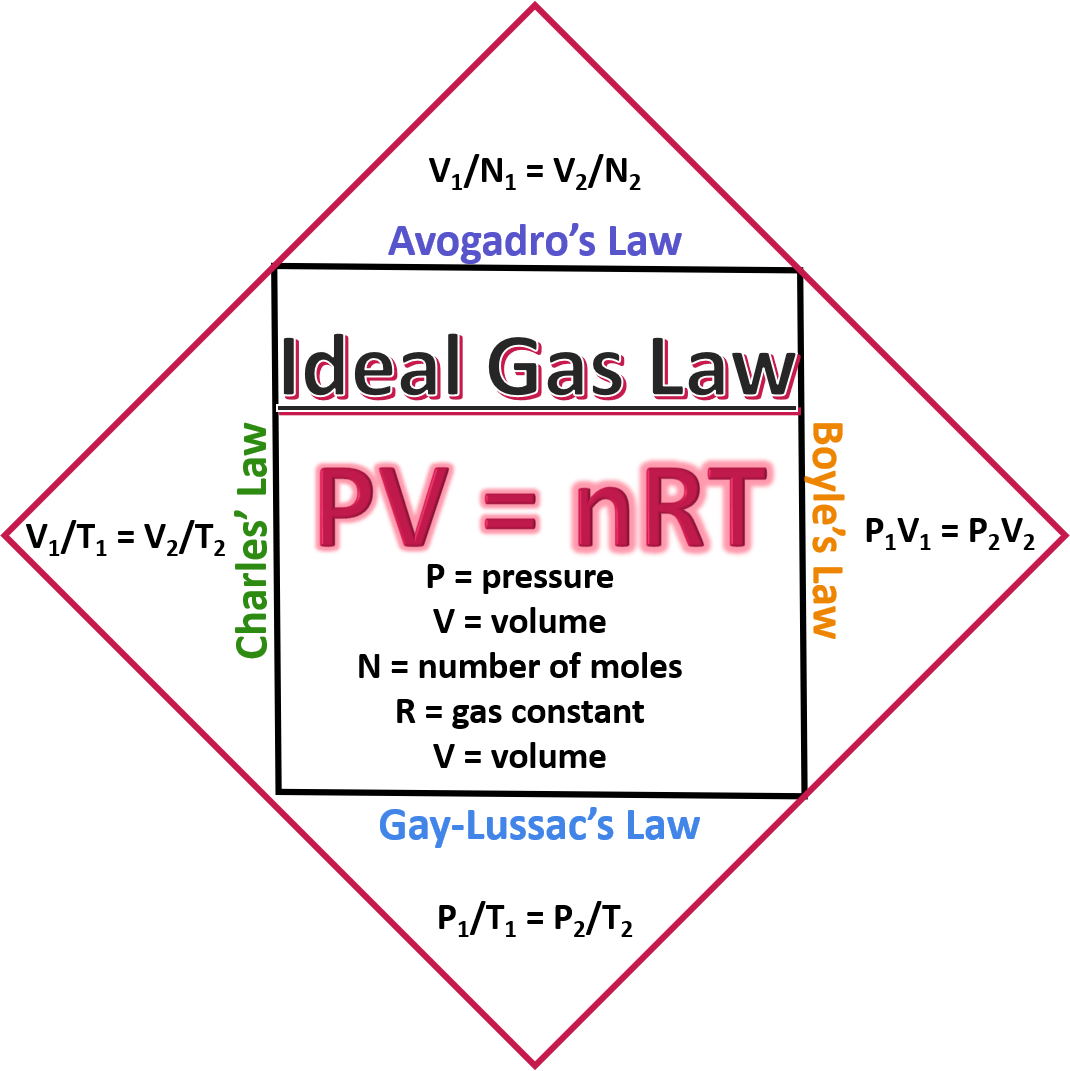
The ideal gas law, a fundamental principle in physics and chemistry, describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas. This law is expressed by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. Among these components, the gas constant R plays a pivotal role in simplifying calculations and understanding the behavior of gases under various conditions.
Understanding the Gas Constant ®
The gas constant R is a proportionality constant that relates the energy of a gas to its temperature. It is defined as the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of one mole of an ideal gas by one degree Kelvin at constant volume. The value of R can be expressed in various units, depending on the context of the calculation. In the International System of Units (SI), R is approximately 8.3145 J/(mol·K). This value is crucial for calculations involving the ideal gas law.
Applications of the Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law has numerous applications across different fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. It is used to predict the behavior of gases under different conditions, such as changes in pressure, volume, or temperature. For example, in chemistry, the ideal gas law can be used to determine the number of moles of a gas produced in a chemical reaction, given the volume of the gas at a known pressure and temperature.
Simplifying Calculations with R
The gas constant R simplifies calculations in several ways:
- Standardization: R provides a standard reference point for calculations involving gases. By using a consistent value for R, calculations become more reliable and comparable across different scenarios.
- Unit Conversion: The gas constant helps in converting between different units of measurement for pressure, volume, and energy. This is particularly useful when dealing with experiments or applications where measurements are taken in different units.
- Predictive Models: By incorporating R into predictive models, scientists and engineers can forecast the behavior of gases under various conditions. This is essential for designing systems that involve gases, such as air conditioning units, internal combustion engines, and chemical reactors.
- Educational Tool: The simplicity and universality of the ideal gas law, facilitated by R, make it an valuable educational tool. It helps students understand complex gas behaviors through straightforward calculations.
Calculational Examples
To illustrate how R simplifies calculations, consider the following examples:
- Calculating the Number of Moles: If you have 10 liters of gas at a pressure of 2 atm and a temperature of 300 K, you can calculate the number of moles (n) using the ideal gas law. Rearranging the equation to solve for n gives n = PV / RT. Substituting the given values and using R = 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K), you can calculate n.
- Finding the Volume: Given the number of moles, pressure, and temperature, you can find the volume of the gas. For instance, for 2 moles of gas at 1 atm and 250 K, using R = 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K), the volume V = nRT / P can be calculated.
Conclusion
The gas constant R is a fundamental component of the ideal gas law, enabling straightforward and accurate calculations of gas properties. Its applications span from basic scientific inquiries to complex engineering designs. By understanding and applying the ideal gas law with R, professionals and students alike can predict and analyze the behavior of gases, contributing to advancements in various fields. Whether for educational purposes or practical applications, the ideal gas law, with R at its core, is an indispensable tool in the sciences.
What is the significance of the gas constant R in the ideal gas law?
+The gas constant R is crucial as it provides a standard reference point for calculations involving gases, facilitating unit conversions, predictive modeling, and educational understanding of gas behaviors.
How does the ideal gas law simplify calculations involving gases?
+The ideal gas law simplifies calculations by providing a straightforward equation (PV = nRT) that relates the pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature of a gas. This equation, along with the gas constant R, allows for the easy calculation of any one of these properties if the others are known.
What are some common applications of the ideal gas law in real-world scenarios?
+The ideal gas law has numerous applications, including chemistry experiments to determine the number of moles of gas produced, engineering designs for systems involving gases (like air conditioning and internal combustion engines), and predictive models for forecasting gas behavior under various conditions.
In conclusion, the ideal gas law, with the gas constant R at its heart, is a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of gases. Its simplicity, universality, and applicability make it an indispensable principle in the sciences, facilitating calculations, educational understanding, and real-world applications with precision and reliability.



