What Is Chart Accounts
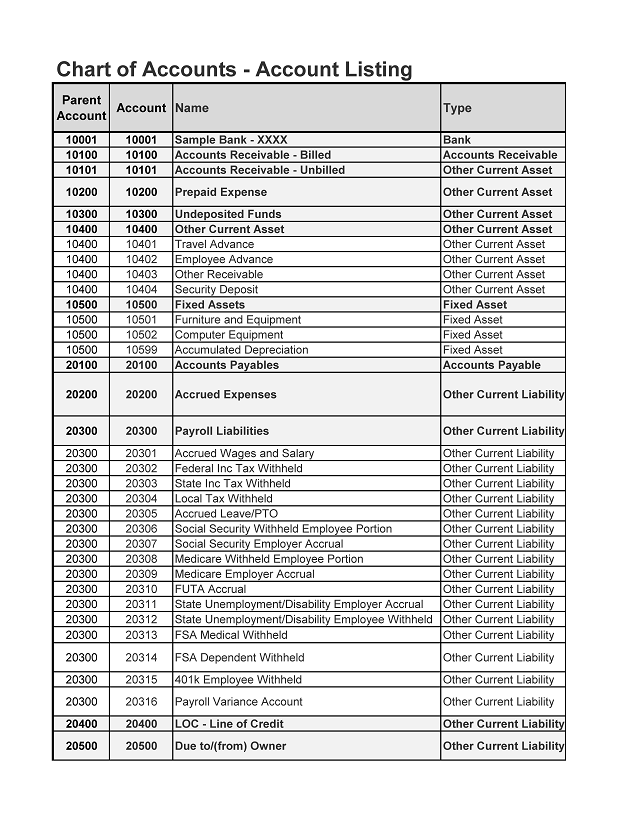
In the realm of financial management and accounting, a chart of accounts (COA) is a fundamental tool that serves as the backbone of a company’s financial record-keeping system. It is a comprehensive list of all the accounts used by a business to record its financial transactions, categorized and organized in a logical and systematic manner. The chart of accounts is essential for maintaining accurate and detailed financial records, which are crucial for making informed business decisions, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Structure of a Chart of Accounts
A typical chart of accounts is structured into various categories or classes, with each category representing a specific type of account. The main categories often include:
- Asset Accounts: These accounts represent what the business owns or is due to receive, such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property, plant, and equipment.
- Liability Accounts: These accounts reflect what the business owes to others, including accounts payable, loans payable, and other debt obligations.
- Equity Accounts: These accounts show the ownership interest in the business, including common stock, retained earnings, and other equity components.
- Revenue Accounts: These accounts record the income earned by the business from its operations, such as sales, service revenue, and interest income.
- Expense Accounts: These accounts represent the costs incurred by the business to generate revenue, including salaries, rent, utilities, and other operating expenses.
Importance of a Chart of Accounts
The chart of accounts plays a pivotal role in financial management for several reasons:
- Organizational Efficiency: It provides a standardized framework for recording and reporting financial transactions, making it easier to manage and analyze financial data.
- Accuracy and Consistency: By using a well-structured chart of accounts, businesses can ensure that financial transactions are recorded accurately and consistently, reducing errors and discrepancies.
- Compliance: It helps businesses comply with accounting standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), and regulatory requirements, such as tax laws.
- Decision Making: The detailed financial information provided by the chart of accounts enables business leaders to make informed decisions about investments, funding, and resource allocation.
- Financial Reporting: It serves as the basis for preparing financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which are essential for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
Creating a Chart of Accounts
Creating a chart of accounts involves several steps, including:
- Identifying Account Types: Determine the types of accounts needed based on the business operations and industry.
- Assigning Account Numbers: Assign unique numbers to each account to facilitate recording and tracking of transactions.
- Categorizing Accounts: Group similar accounts into categories for easier management and reporting.
- Reviewing and Updating: Regularly review the chart of accounts and update it as necessary to reflect changes in the business or accounting requirements.
Technology and Chart of Accounts
Modern accounting software and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have significantly simplified the management of a chart of accounts. These systems allow for the easy creation, modification, and maintenance of account structures, as well as the automation of many accounting processes, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
In conclusion, a chart of accounts is a critical component of a company’s financial infrastructure, providing a systematic approach to financial record-keeping and reporting. Its importance extends to facilitating accurate financial analysis, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and supporting strategic decision-making. As businesses evolve and grow, their chart of accounts must also adapt to reflect changing needs and circumstances, underscoring the dynamic nature of financial management in today’s fast-paced business environment.
For small businesses or startups, it's essential to establish a well-structured chart of accounts from the outset. This foundation will support the company's growth by providing a clear, organized framework for financial management and decision-making.
What is the primary purpose of a chart of accounts?
+The primary purpose of a chart of accounts is to provide a systematic and organized way of recording and reporting financial transactions, facilitating accurate financial analysis and compliance with accounting standards.
How often should a chart of accounts be updated?
+A chart of accounts should be regularly reviewed and updated as necessary to reflect changes in the business operations, accounting policies, or regulatory requirements.
By understanding and effectively utilizing a chart of accounts, businesses can streamline their financial management processes, enhance decision-making capabilities, and ensure transparency and accountability in their financial reporting practices.



