What Is Hydrogen Bonding In Water? A Clear Explanation
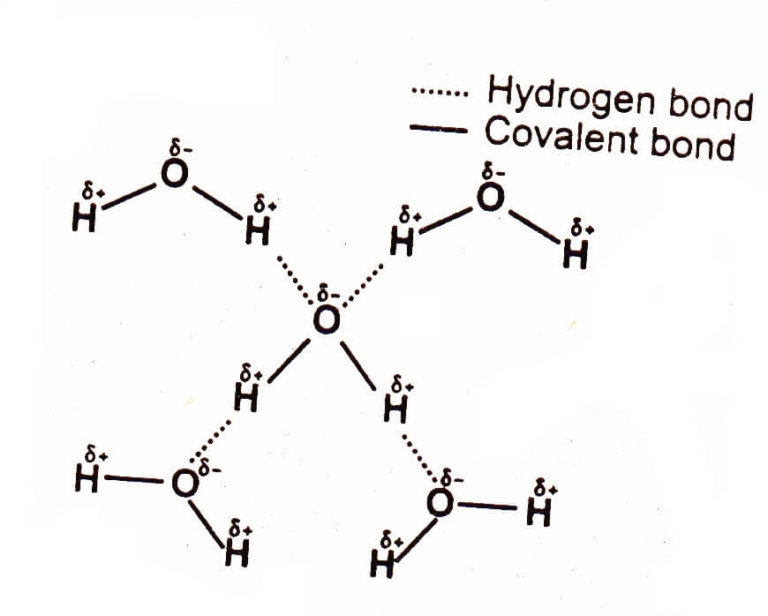
Hydrogen bonding in water is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains the unique properties of water, making it an essential component of life on Earth. To understand hydrogen bonding, let’s first explore the molecular structure of water.
Water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, arranged in a bent or V-shape. The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms, meaning it has a greater tendency to attract electrons. This results in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom. The unequal sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms creates a polar molecule, with a slightly positive charge on one side (hydrogen atoms) and a slightly negative charge on the other side (oxygen atom).
Hydrogen bonding occurs when the partially positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the partially negative oxygen atom of another water molecule. This attraction is a type of intermolecular force, which is weaker than the covalent bonds within the water molecule itself. Hydrogen bonds are relatively strong compared to other types of intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces, but are still much weaker than covalent bonds.
The unique properties of water, such as its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve a wide variety of substances, can be attributed to the presence of hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonds between water molecules create a network of attractions that give water its structure and properties.
One of the most significant effects of hydrogen bonding in water is its ability to resist temperature changes. Hydrogen bonds help to absorb and release heat energy, allowing water to regulate its temperature and maintain a relatively stable environment. This property is essential for life on Earth, as it helps to regulate the climate and maintain a stable environment for living organisms.
In addition to its role in temperature regulation, hydrogen bonding also plays a crucial role in the structure and function of biological molecules, such as proteins and DNA. Hydrogen bonds help to stabilize the structure of these molecules, allowing them to perform their biological functions.
To further illustrate the importance of hydrogen bonding in water, let’s consider a few examples:
- Surface tension: Hydrogen bonds between water molecules at the surface of a body of water create a “skin” that allows certain insects, such as water striders, to walk on water.
- Boiling point: The high boiling point of water is due to the energy required to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules, allowing water to boil at a higher temperature than would be expected based on its molecular weight.
- Dissolving substances: Hydrogen bonds between water molecules and other substances, such as salts and sugars, allow water to dissolve a wide variety of substances, making it an excellent solvent.
In conclusion, hydrogen bonding in water is a fundamental concept that explains the unique properties of water, making it an essential component of life on Earth. The attraction between partially positive hydrogen atoms and partially negative oxygen atoms creates a network of hydrogen bonds that give water its structure and properties, regulating temperature, and facilitating the function of biological molecules.
Hydrogen bonding is not unique to water and can occur in other substances, such as ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. However, the strength and prevalence of hydrogen bonds in water make it an exceptional substance with properties that are essential for life.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between a hydrogen bond and a covalent bond?
+A hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules, whereas a covalent bond is a chemical bond that occurs within a molecule. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds and are responsible for the unique properties of water.
How does hydrogen bonding affect the boiling point of water?
+Hydrogen bonding between water molecules requires energy to break, allowing water to boil at a higher temperature than would be expected based on its molecular weight. The energy required to break these bonds is released as the water molecules transition from a liquid to a gas state.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in the structure and function of biological molecules?
+Hydrogen bonds help to stabilize the structure of biological molecules, such as proteins and DNA, allowing them to perform their biological functions. These bonds can also facilitate interactions between molecules, enabling them to recognize and bind to specific targets.
By understanding the role of hydrogen bonding in water, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of this essential substance, and how it supports life on Earth. Whether it’s regulating temperature, facilitating biological processes, or simply quenching our thirst, water is an incredible resource that deserves our appreciation and respect.



