When Is A Full Moon? Lunar Calendar Inside
The full moon, a phenomenon that has captivated human imagination for centuries, occurs when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, resulting in the entire face of the Moon being illuminated by the Sun’s light. This event happens once every 29.5 days, which is the approximate length of a lunar cycle. But what exactly is a lunar cycle, and how does it impact the occurrence of full moons?
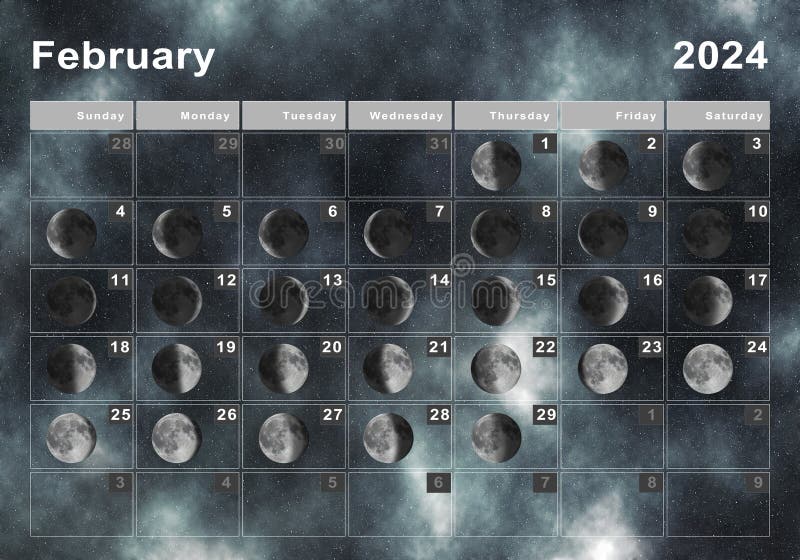
To understand the timing of full moons, it’s essential to delve into the lunar calendar, a system that has been used for millennia to track the phases of the Moon. The lunar calendar is based on the cycles of the Moon, with each month beginning on the new moon. There are several types of lunar calendars, including the synodic month, the sidereal month, and the anomalistic month, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
The synodic month, which is the most commonly used lunar cycle, is the time it takes for the Moon to return to the same phase, approximately 29.5 days. This cycle is divided into eight distinct phases: new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent. Understanding these phases is crucial for predicting the timing of full moons, as well as other lunar events.
One of the most significant factors affecting the timing of full moons is the Moon’s elliptical orbit around the Earth. The Moon’s distance from our planet varies throughout the month, with the closest point, called perigee, occurring when the Moon is about 363,300 kilometers away. Conversely, the farthest point, apogee, occurs when the Moon is approximately 405,500 kilometers away. This variation in distance impacts the Moon’s apparent size in the sky, with the Moon appearing larger at perigee and smaller at apogee.
Another crucial aspect of the lunar calendar is the concept of lunar nodes, which are the points where the Moon’s orbit intersects the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. There are two types of lunar nodes: the ascending node, where the Moon crosses from the Southern Hemisphere to the Northern Hemisphere, and the descending node, where the Moon crosses from the Northern Hemisphere to the Southern Hemisphere. The lunar nodes play a vital role in determining the timing of eclipses, which can only occur when the Moon is at or near one of the nodes.
Full moons have been a subject of fascination and mythological significance across various cultures. In many ancient societies, full moons were associated with ritualistic practices, harvest festivals, and spiritual ceremonies. For example, the Chinese Mid-Autumn Festival, which falls on the 15th day of the eighth lunar month, is a celebration of the full moon and the harvest season. Similarly, the Native American tribes have a rich tradition of full moon ceremonies, which often involve music, dance, and storytelling.
The full moon has also been linked to various effects on human behavior, including increased crime rates, higher hospital admissions, and even changes in sleeping patterns. While these claims are often anecdotal and lack concrete scientific evidence, they do reflect the profound impact that the full moon has on our collective psyche.
In addition to its cultural and mythological significance, the full moon has also been the subject of scientific study. Astronomers and physicists have long been fascinated by the Moon’s gravitational pull on the Earth’s oceans, which results in the rise and fall of sea levels, known as tides. The full moon’s gravitational influence is also responsible for the stabilization of the Earth’s axis, which is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees.
To further understand the complexities of the lunar calendar and the full moon, let’s examine some specific examples. For instance, the “Blue Moon,” which occurs when there are two full moons in a single month, is a rare and fascinating event. This phenomenon happens because the lunar cycle and the calendar year are not perfectly synchronized, resulting in an extra full moon every 2.7 years.
In conclusion, the full moon is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has captivated human imagination for centuries. By exploring the lunar calendar, the Moon’s elliptical orbit, and the concept of lunar nodes, we can gain a deeper understanding of the timing and significance of full moons. Whether viewed through the lens of cultural mythology, scientific inquiry, or personal fascination, the full moon remains an enduring and awe-inspiring spectacle in the night sky.
FAQ Section:
What is the average distance of the Moon from the Earth during a full moon?
+The average distance of the Moon from the Earth during a full moon is approximately 384,400 kilometers.
How often does a Blue Moon occur?
+A Blue Moon occurs approximately every 2.7 years, resulting in an extra full moon in a single month.
What is the significance of lunar nodes in the timing of eclipses?
+Lunar nodes are crucial in determining the timing of eclipses, as they mark the points where the Moon’s orbit intersects the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, allowing for the alignment necessary for an eclipse to occur.
How do full moons impact the Earth’s oceans?
+Full moons have a significant impact on the Earth’s oceans, resulting in the rise and fall of sea levels, known as tides, due to the Moon’s gravitational pull.
What is the cultural significance of full moons in various societies?
+Full moons have been a subject of fascination and mythological significance across various cultures, often associated with ritualistic practices, harvest festivals, and spiritual ceremonies.
How does the full moon affect human behavior?
+While there is limited scientific evidence, full moons have been linked to various effects on human behavior, including increased crime rates, higher hospital admissions, and changes in sleeping patterns, although these claims are often anecdotal and require further research.



